Answer of November 2016
For completion of the online quiz, please visit the HKAM iCMECPD website: http://www.icmecpd.hk/
Clinical History:
A 59-year-old lady presented with shortness of breath. She was a non-smoker. Patient’s brother and sister had history of pneumothoraces. Patient’s brother also had CT thorax done previously showing bilateral lung cysts. CXR and CT thorax were performed.
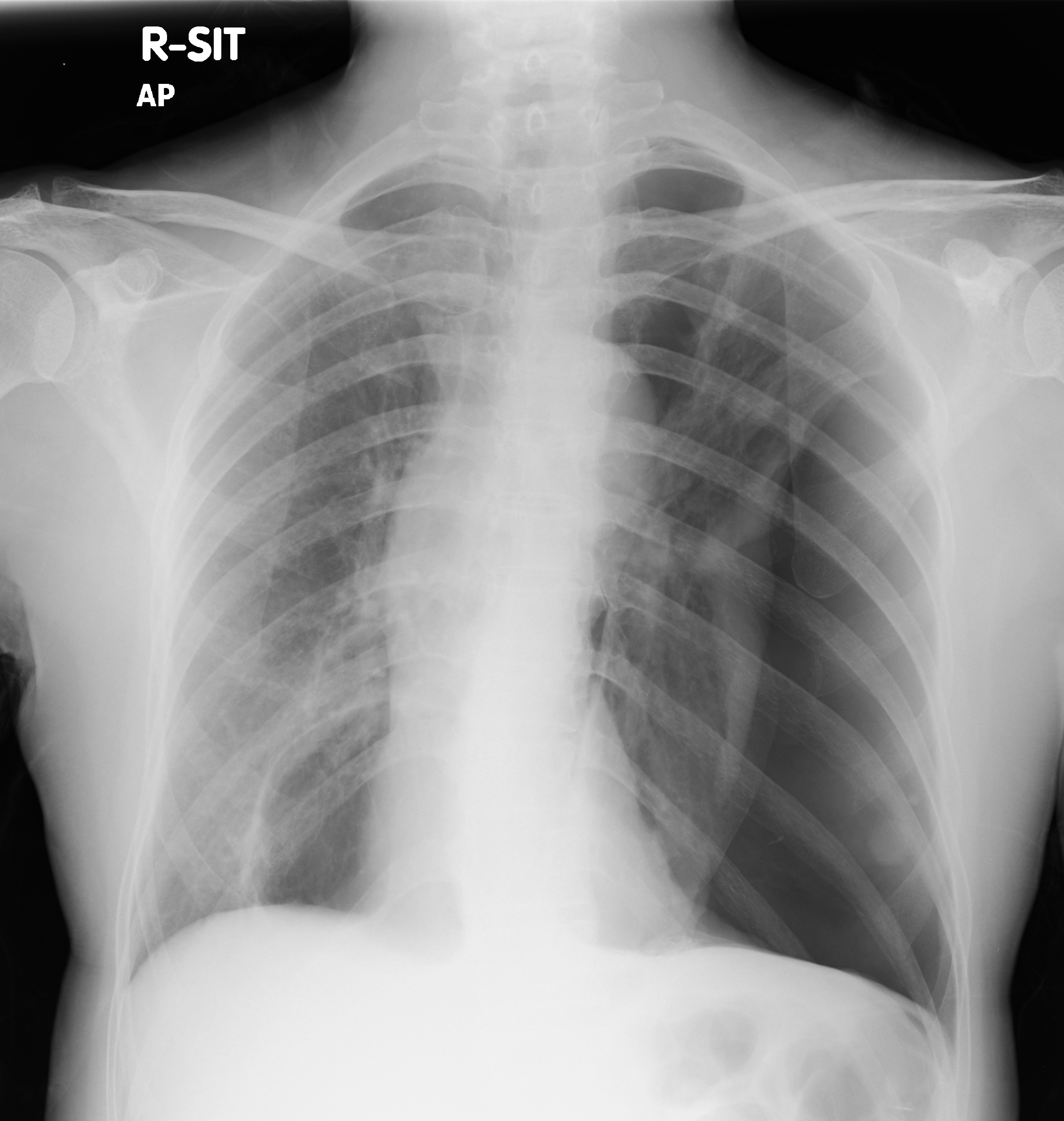
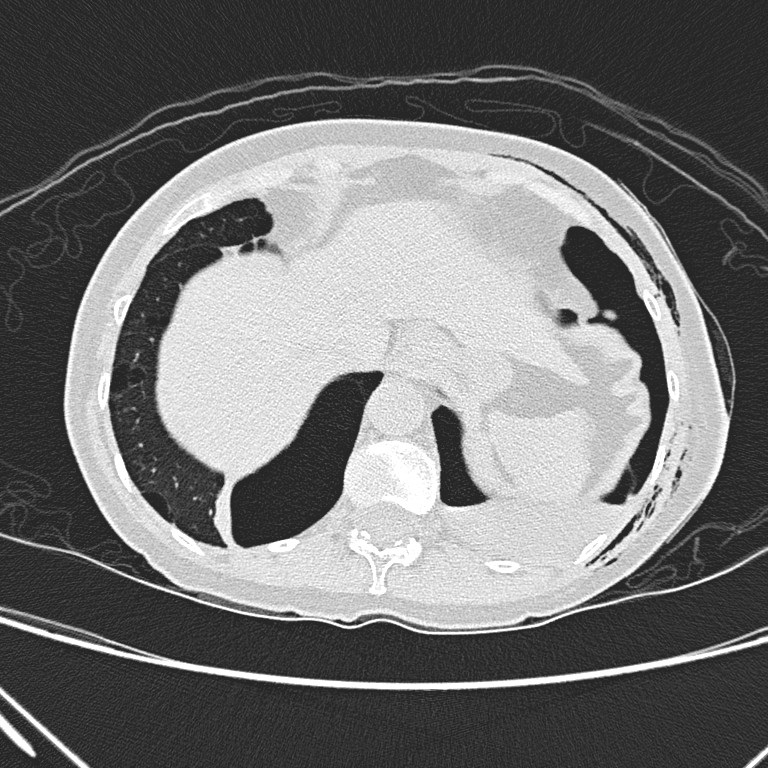
Initial CXR
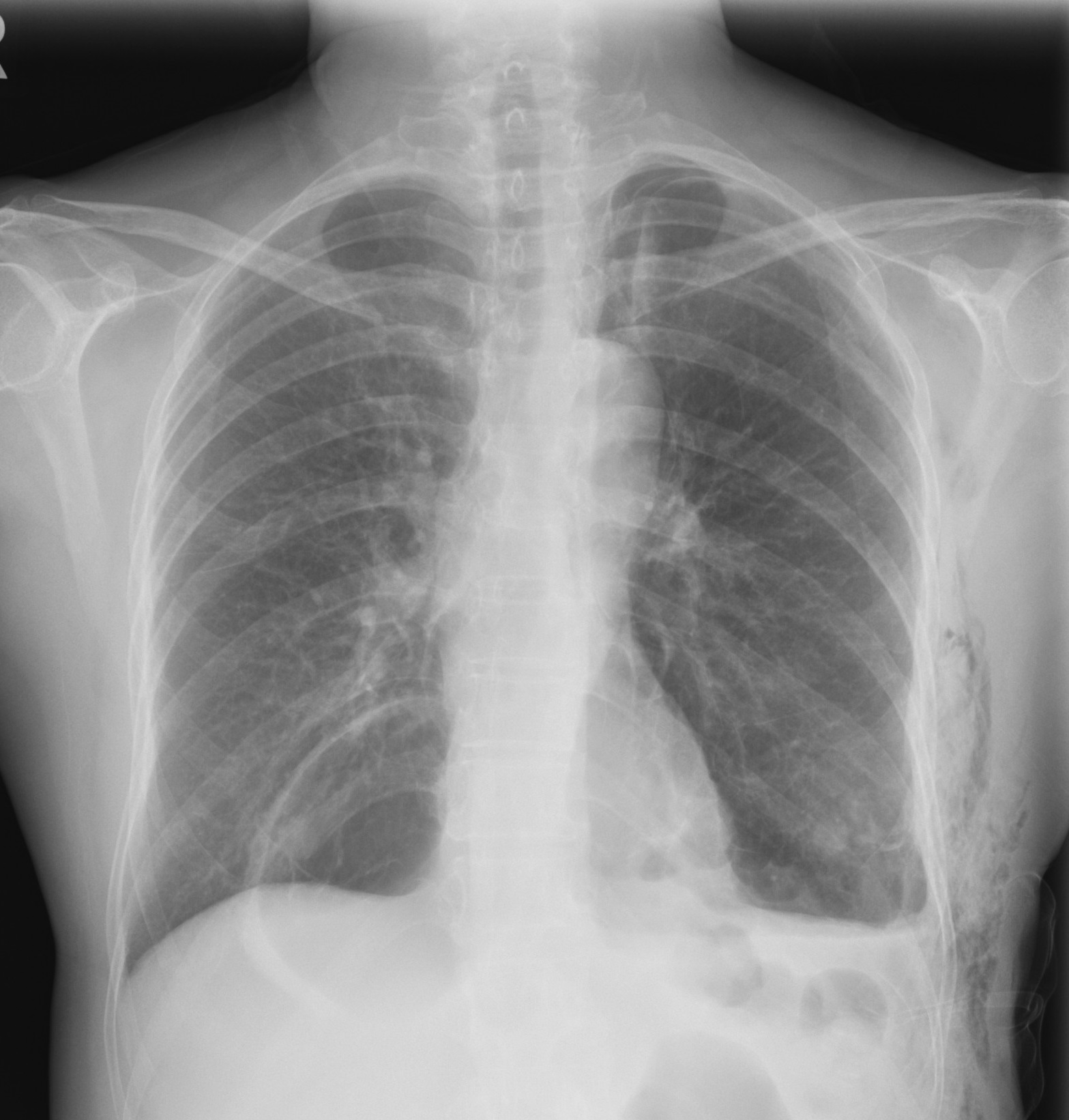
CXR after insertion and removal of chest drain
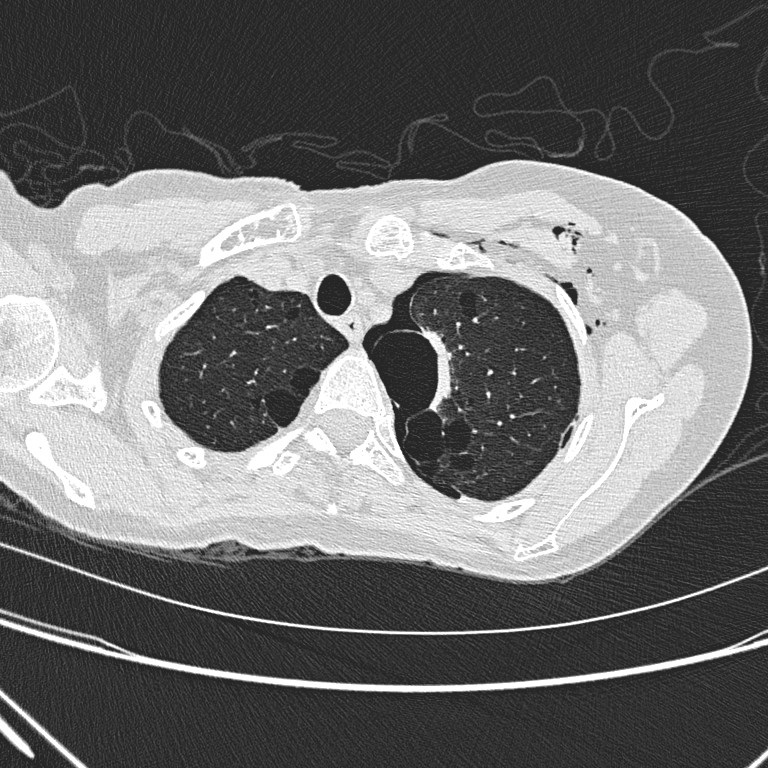
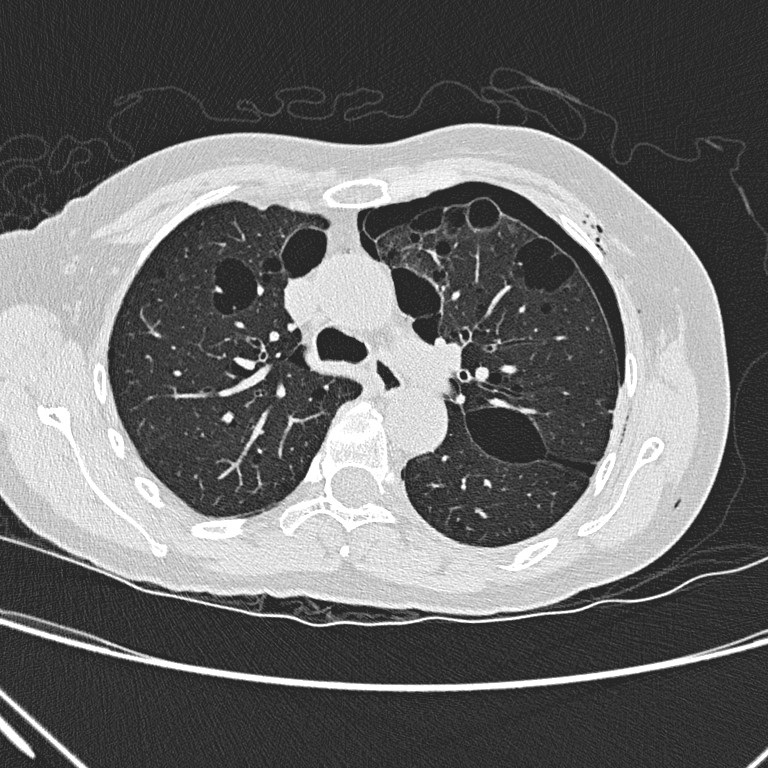
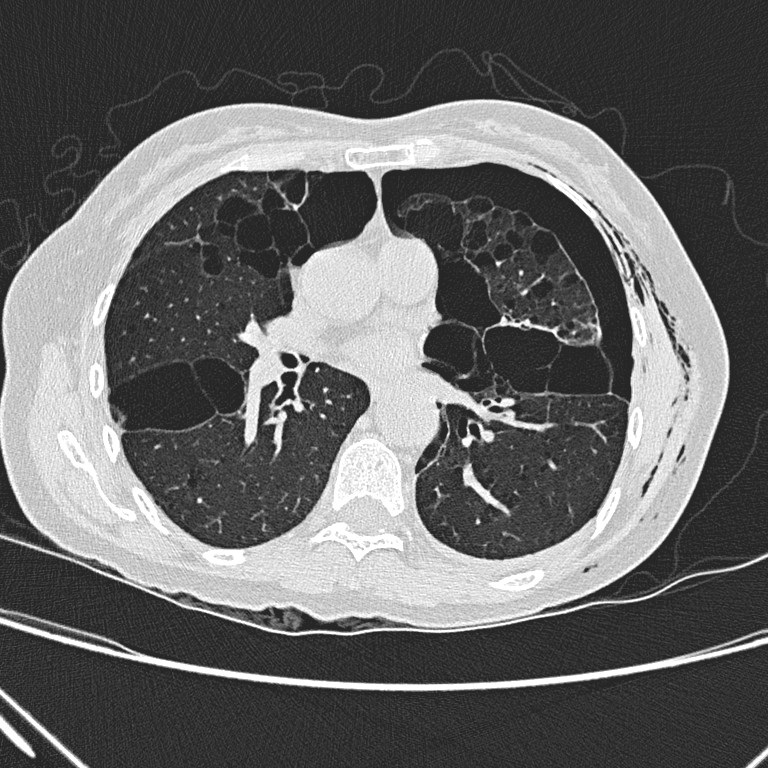
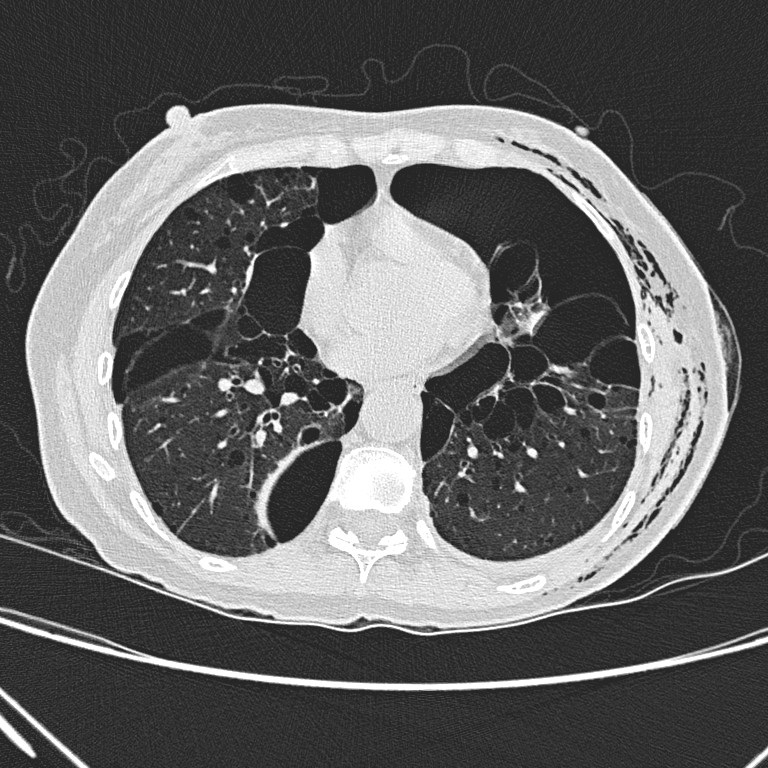
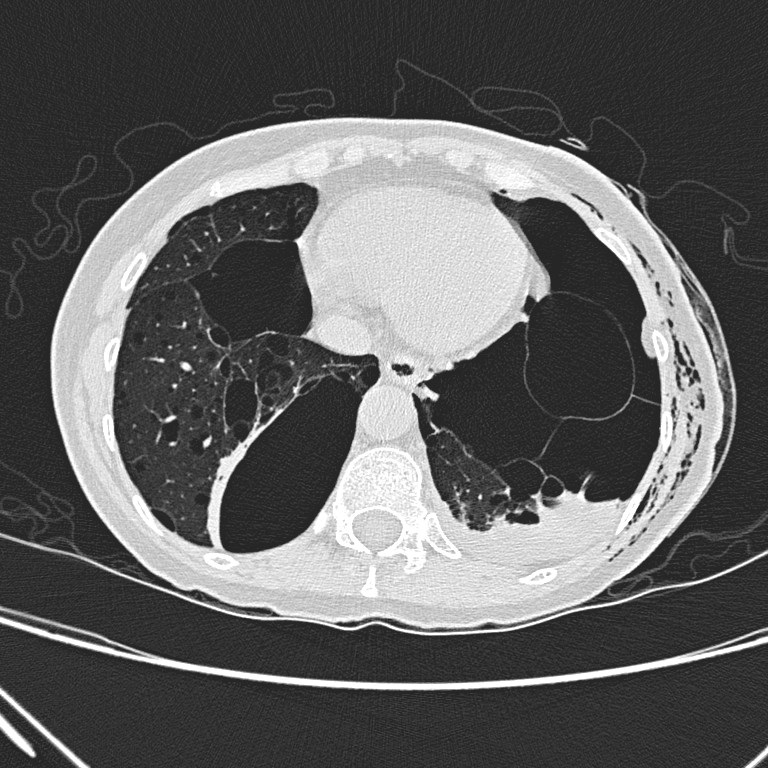
Non-contrast CT thorax
Diagnosis:
Birt-Hogg-Dube Syndrome
Discussion:
Initial CXR shows
a large left pneumothorax with mild mediastinal shift towards the right side. A
large cystic lesion is seen in medial right lower zone.
Subsequent CXR
after chest drain better illustrates the large cystic lesion in medial right
lower zone with slightly thickened wall.
Non-contrast CT
thorax shows left hydropneumothorax with subcutaneous emphysema. There are
multiple oval or lentiform thin-walled cysts of various sizes in both lungs
with lower zonal predominance. Apparent wall thickening of the largest cyst in
medial basal segment of right lower lobe is likely due to compressive collapse
of adjacent lung parenchyma. No lung nodule or ground-glass opacity is seen.
Differential
diagnoses of cystic lung disease include Langerhan’s cell histiocytosis (LCH),
lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM), neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) and lymphocytic
interstitial pneumonitis (LIP).
Langerhan’s cell
histiocytosis (LCH) usually occurs in young adults with smoking history. The
cysts are of bizarre shapes. There will also be centrilobular nodules and
reticular densities/ thickening of interlobular septa in the lung.
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
(LAM) usually affect women of child-bearing age. Thin-walled cysts of similar
sizes are usually seen throughout the lung without zonal predominance.
Pulmonary
manifestations of neurofibromatosis type 1 consist of peripheral nodules, lower
zone fibrosis and upper zone large bullae.
Lymphocytic
interstitial pneumonitis (LIP) has features including perivascular thin-walled
cysts, ill-defined centrilobular nodules, ground-glass opacities and
interlobular septal thickening.